- Archive
- Pinglin Project
- Coursework Posters
Coursework Posters
On-site Workshop
Coursework documentation.
Global Warming and Tea
因應氣候變遷的影響,透過葉片生長成熟度的「積溫模型」來加強坪林茶產業採收季節的預測。並且透過採茶預測模型的建構和草生栽培管理,希望可以有助有機茶農降低採收與除草的人力成本。

Happy Tea Plantation
因應坪林地區氣候變遷變化,推廣有機與環境友善農法,再加上採茶人口老化,建構一生態打工網站平台來媒合都市年輕人力,透過宣傳聯繫會員,經由入門活動,開始協助坪林茶農在採茶季時,協助打工,從事茶園田間管理與有機除草工作。並透過生態導覧解說活動,將坪林的環境介紹給都市居民。

Design of Tea-Leaf Plucking Management
觀察到影響茶品質的最大因素是茶葉採收時的天氣狀態,若需要調派額外人力則更需要負擔成本的風險。因此,模擬一人力調派與氣候顧問公司,從坪林氣象資料統計與預測採茶季節時的天氣,作出調派人力的建議,以降低風險。

Tea Master: Bluemagpie
為了推廣坪林當地茶葉,設計製作了手機遊戲軟體APP,模擬與學習製茶過程,讓年輕族群可以透過現代數位產品而認識坪林當地茶葉的優點。

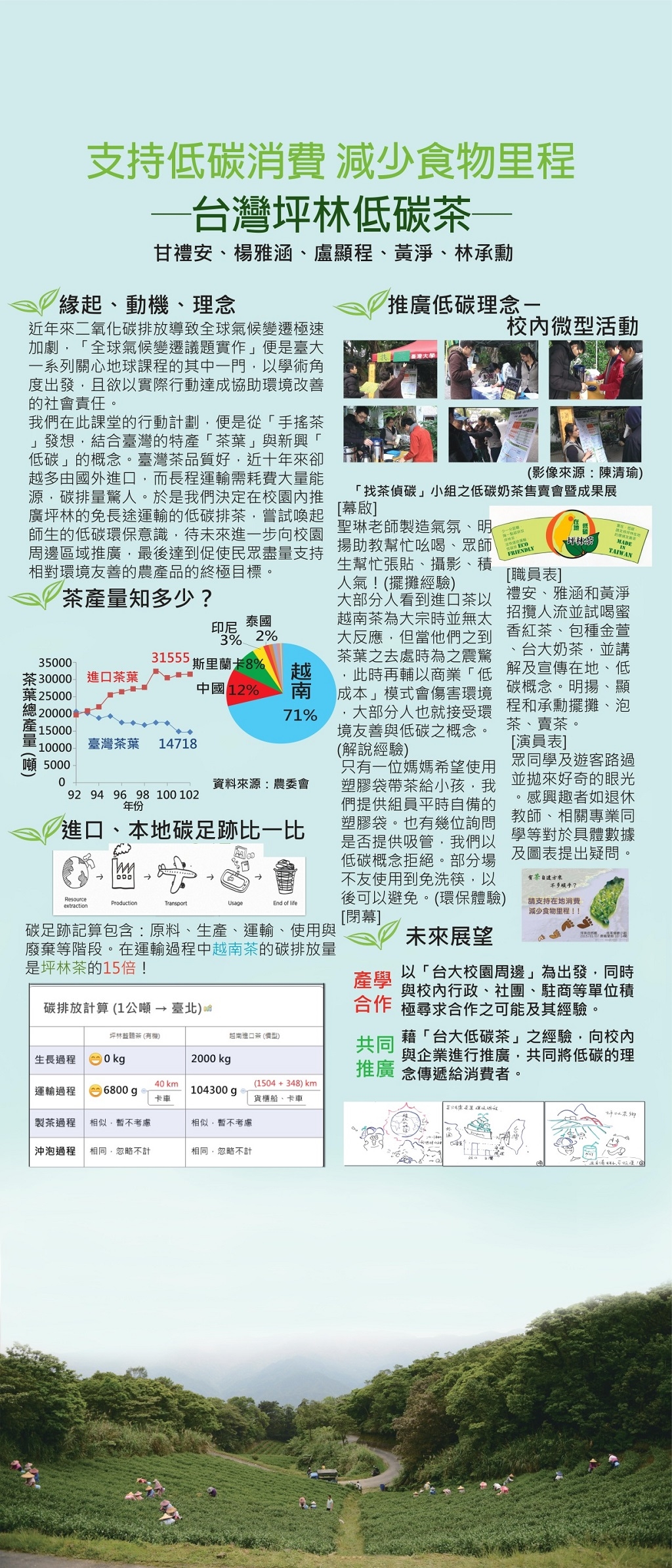
Low-Carbon Tea Production in Pinglin, Taiwan
從臺灣茶葉生產與進口數量與價格的差異來設想推廣在地茶對氣候變遷與環境的影響。開始思考計算茶產業的碳足跡,從生長、製茶、運輸、沖泡等各階段所消耗的碳排放量。進而設計與推廣實驗性商品,並從身邊做起,由台大校園出發,推出「坪林茶+台大牛奶」成為「低碳茶」來推廣「在地消費」,鼓勵消費者、商家使用在地茶葉,減少進口茶的運輸碳排放量。計劃目的在於試算並推廣「低碳茶」理念,從消費者對選用茶產品的行為開始分析,除了茶產品的價格之外,還可以考量茶產品的碳足跡。從「理念推廣」開始做起,嘗試改變以成本與價錢為考量的大眾茶消費市場。並影響廠商對產品生命週期的碳排放計算與評估。
Urban-Rural Schools and Intercollegiate Exchanges
觀察到現行城鄉交流多流於形式,而少有實質意義,然而城鄉之間的差距的確是資源與環境不平衡的問題根源。同學開始思考理想的城鄉交流應該為何?小組計畫書構想:以坪林為基地、將環境教育紮根。推動行動策略規劃,以坪林國小為基地推展城鄉交流。主要對象是新北市坪林國小、臺北都會區小學的就學學童。設定目標:(一)認知層次:提升對自然的敏銳度,如:氣候變遷對環境的影響。(二)鄉土層次:換個角度認識家鄉並賦予新價值。(三)政策層次:將城鄉彼此的困境轉化為互補。

People, Streams, Flows
經過調查與統整,拍攝15分鐘短片,來綜觀坪林發展的歷史脈絡,在既有茶鄉印象的背後,顯現經濟與環境之間的衝突。藉由訴說坪林的故事,使大家了解坪林從興盛、受創、致力與自然環境共存的歷程。影片描述了坪林環境變遷過程,也向前展望坪林環境未來。

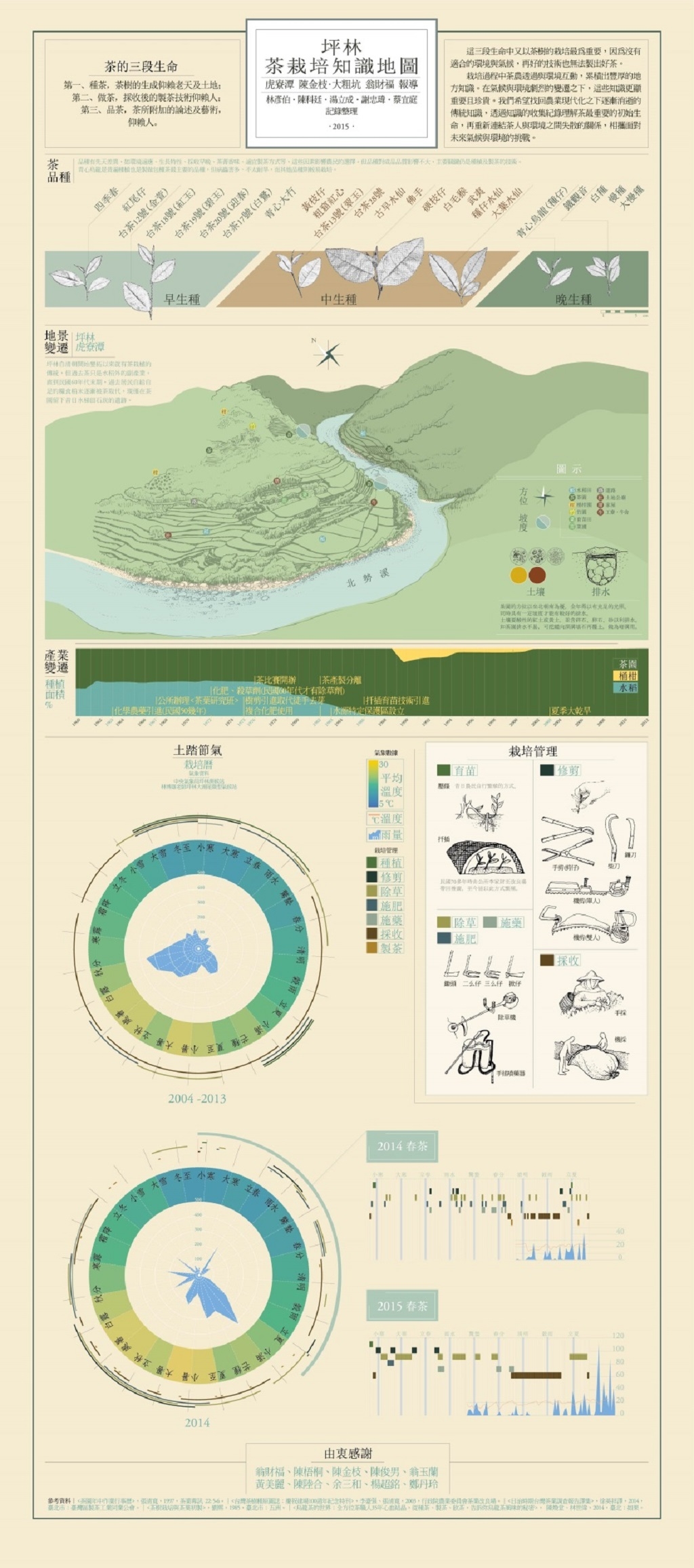
Map of Tea Knowledge
由修課學生繪製的坪林茶栽培知識地圖中的節氣圖可知,2014年的雨量(黃色部分)比前十年在某季節的平均量多,但全年雨量卻比前十年平均量少,由此可知,氣候變遷導致急降雨的情形發生,而雨量對茶葉栽種特別是採茶及製茶時的溫溼度非常重要。為因應這種情況,我們可以提供這門課所蒐集到的相關溫度、雨量等數據資料給茶農,讓茶農預估最適合採茶及製茶的時機。也可以根據這個資料來規劃改變栽種方式,比如說利用哪種地形來種植,是山坡地或梯田,或選擇集水或灌溉等方式。我們從現在開始蒐集資料及分析,以期在未來讓茶農根據我們提供的數據及分析結果來採用最有利的栽種方式。
Full Report
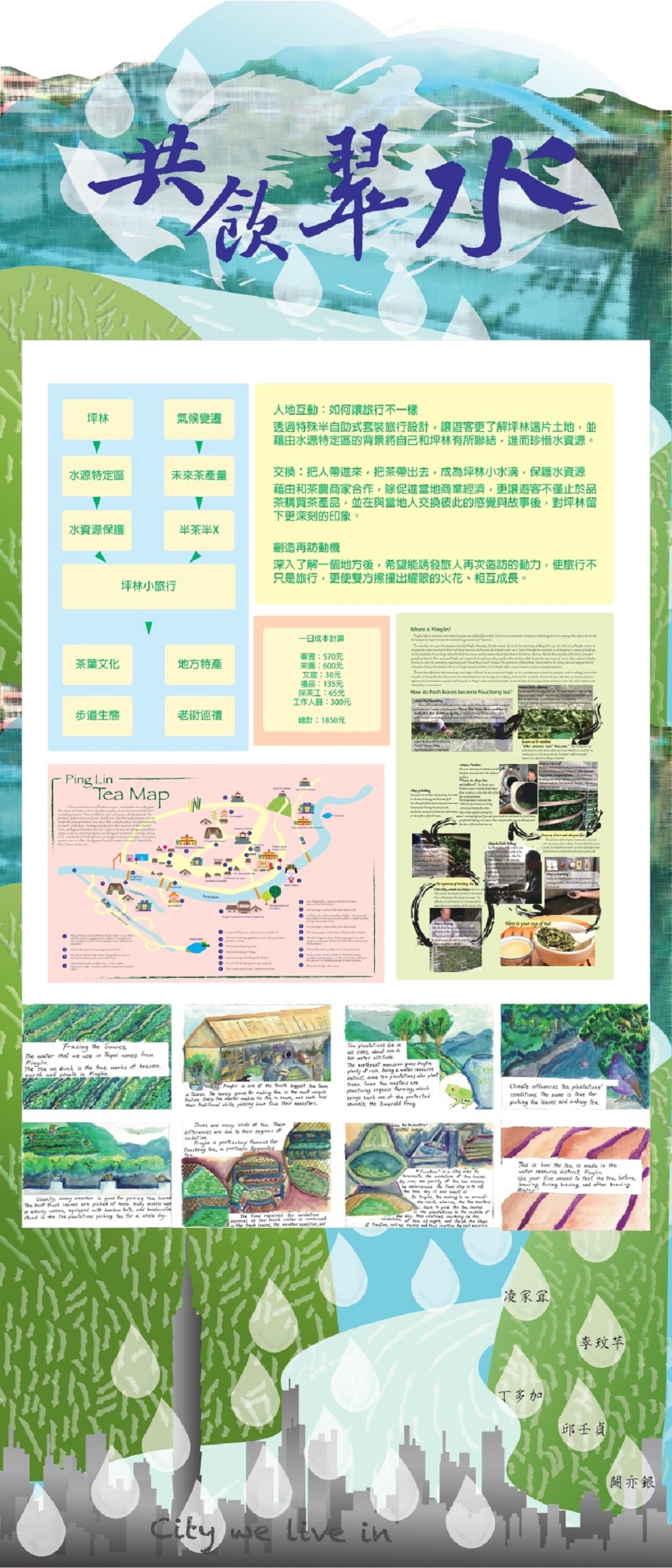
Design a Tour Package
共飲翡翠水是完全由學生設計將坪林介紹給國際外賓的一個活動。學生設計的坪林小手冊、自繪坪林地圖,將坪林的茶產業、人文、生態都向外賓做了非常仔細的介紹,並聽取回饋意見,也是提供給當地居民一種觀光業搭配茶產業的彈性運作另類模式。
Designing for Centre-Space as Interactive Space Tea Factory

Olfactory Experience of Space

Transition Region Planning for Psychological Adaptation

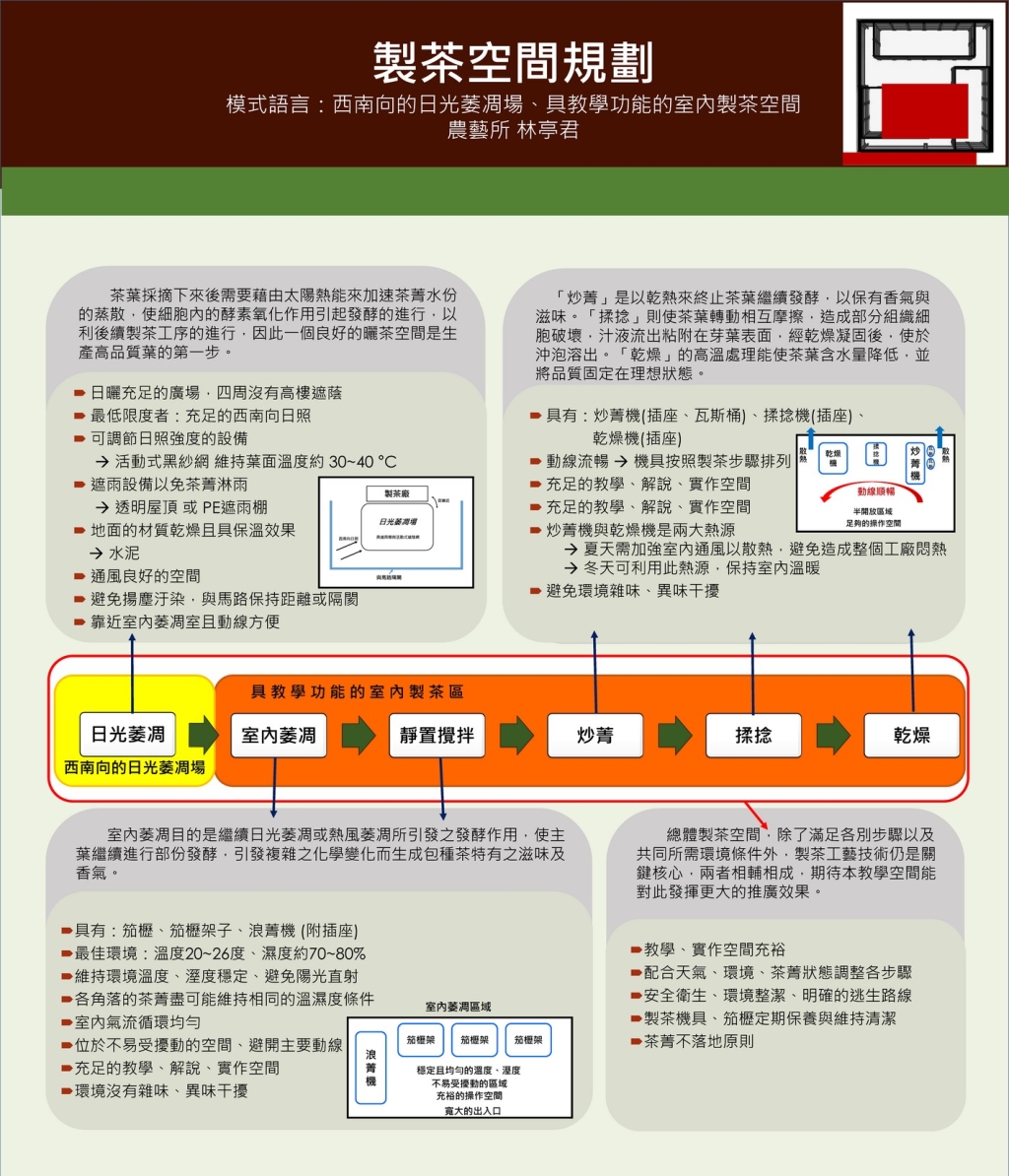
Space Planning for Tea Factories
Adaptive Strategies for Temperature and Humidity Control

多層次調適空間

茶水之道

Documentary of Pinglin Tea Farmers under Climate Challenges

Network of Pattern Language

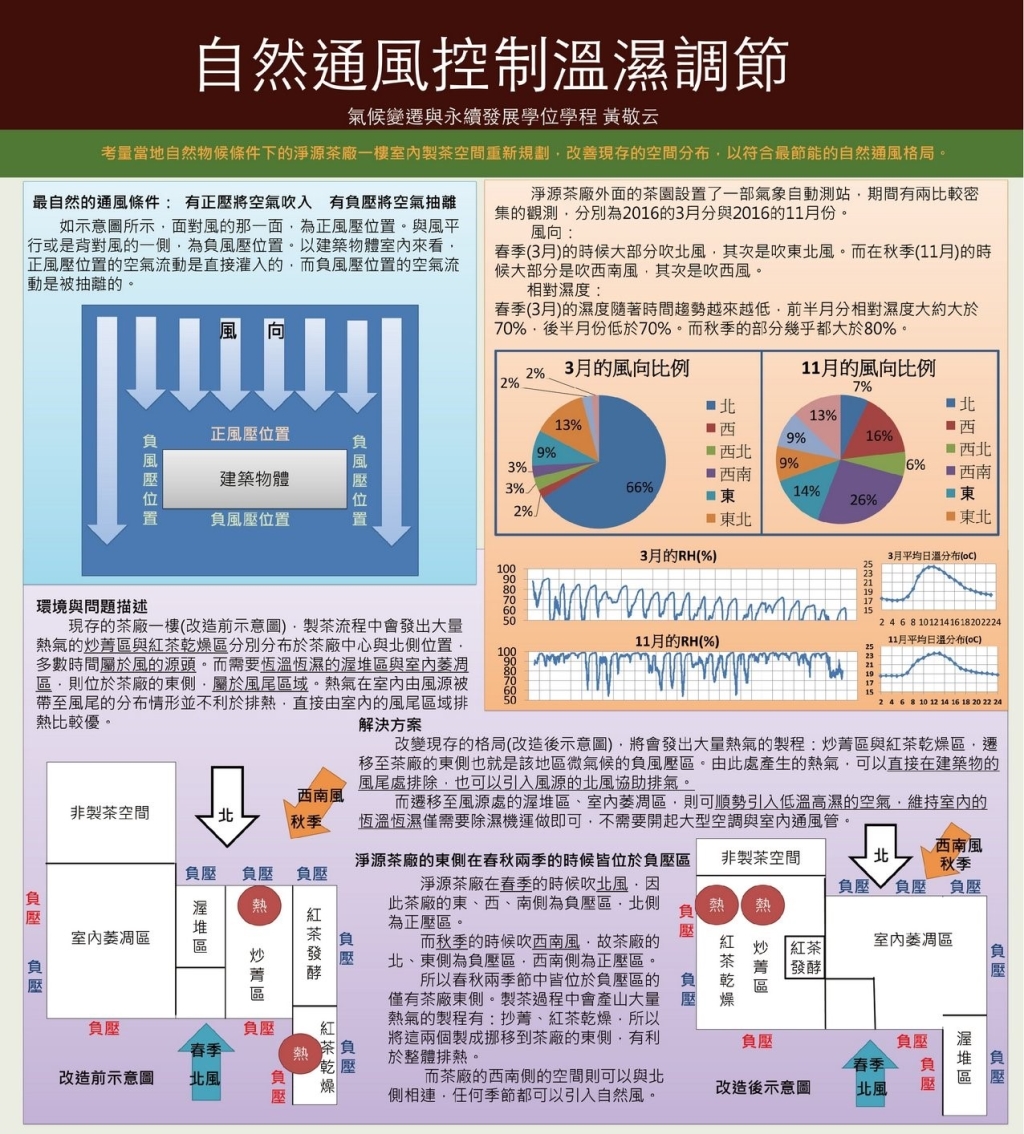
Apply Natural Ventilation Solutions
Aloft Ventilation of Drying Room

Vertical Space Integration of Tea Manufacturing Process

Plant Curtains

Natural Lighting Solutions in Jing-Yuan Tea Factory

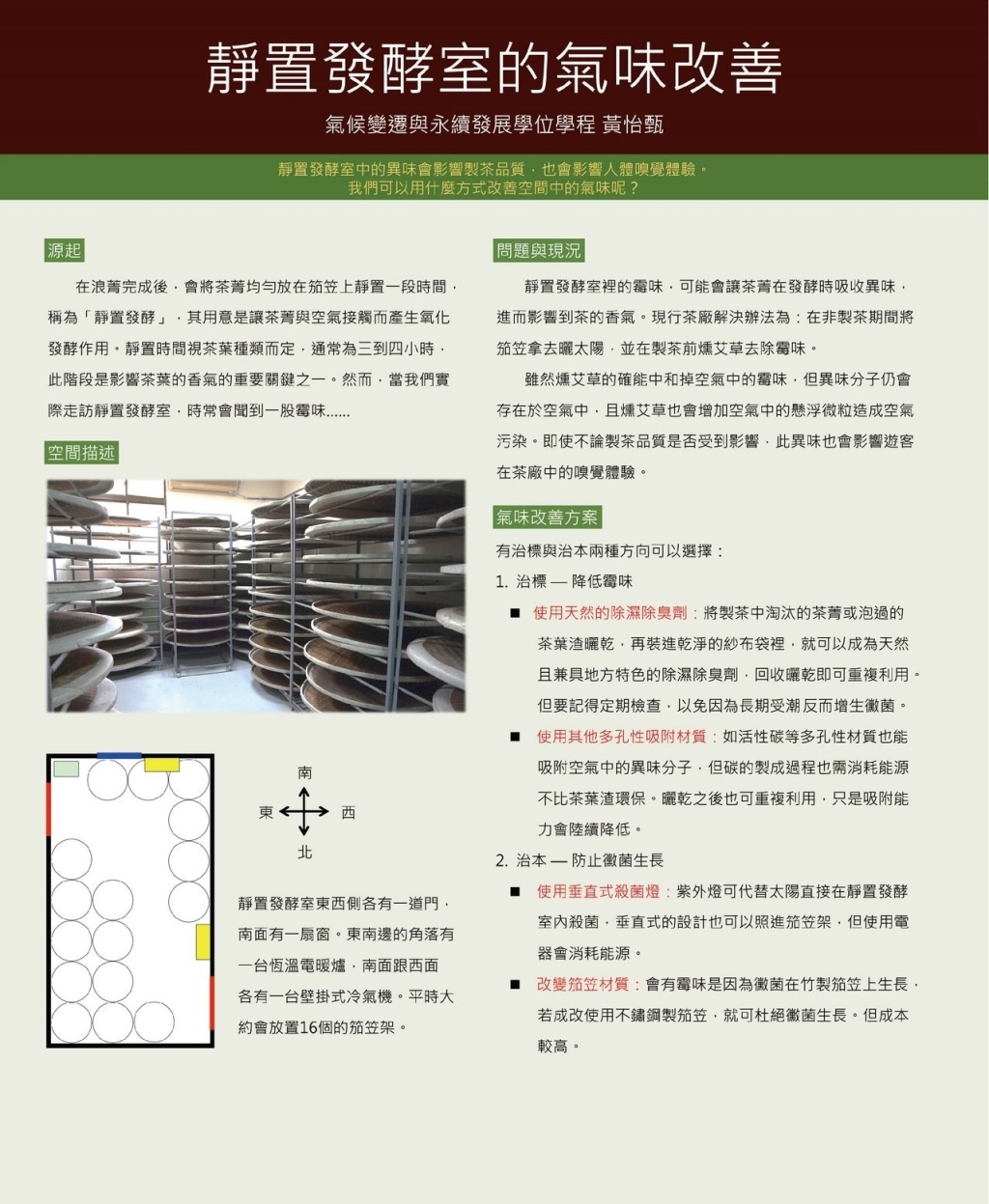
Decreasing Fermentation Smell Indoors
Proverbs and Climate Change
The primary industry is facing a direct impact of the climate and environmental change. In order to be close to the local industry, this study targeted Pinglin, “the tea’s home of the north”, as the region of the study. It is found that the time for tea leaf picking changed drastically, which increases the difficulty of division of labour between tea picking and making. On top of the change of modern people’s living habits, Pinglin’s tea industry now faces a predicament of decrease in market demand and difficulty in producing teas at the same time.
This study uses meteorological data, field study records to analyze and verify Pinglin’s ancient proverbs which are very familiar to the locals; the study also discusses whether these proverbs are still suitable for the present time being and the potential impact it may bring to the Pinglin’s local tea industry. In addition, it derives a new set of climate proverbs that are suitable to the local’s current condition to adapt to climate change. This study promotes climate-related knowledge with the method of being close to the locals and wishes to let the Pinglin’s tea industry and the residents to understand relevant knowledge of the climate change, and to infuse new energy to Pinglin region. Hope to evoke the locals to focus on the relationship between man and the land, and to care about the weather while discussing to each other how man and the land can interact to indirectly reach the harmony between the residents. Furthermore, the goals of adapting to the climate change and sustainability development can be reached.
This study verified the following proverbs: “Tang zhe ti goeh-thau, ou koa ti ni-tau; Tang zhe ti tiong-yang, bo she koh bo sng; Tang zhe ti goeh-boe, ou koa chia li goeh” , “Li goeh chheng beng ban te chheng-beng jit, sa goeh chheng-beng ban te ban chap kang” , “Lip-chhun loh-ho thau chheng-beng”, “Jit thau sang suann, bina ah zai tsang sui tei lai mah”, and “Chhun bong phak si kui, ha bong cho toa bhui”.
Full Report

Tea Growers' Drought Solutions

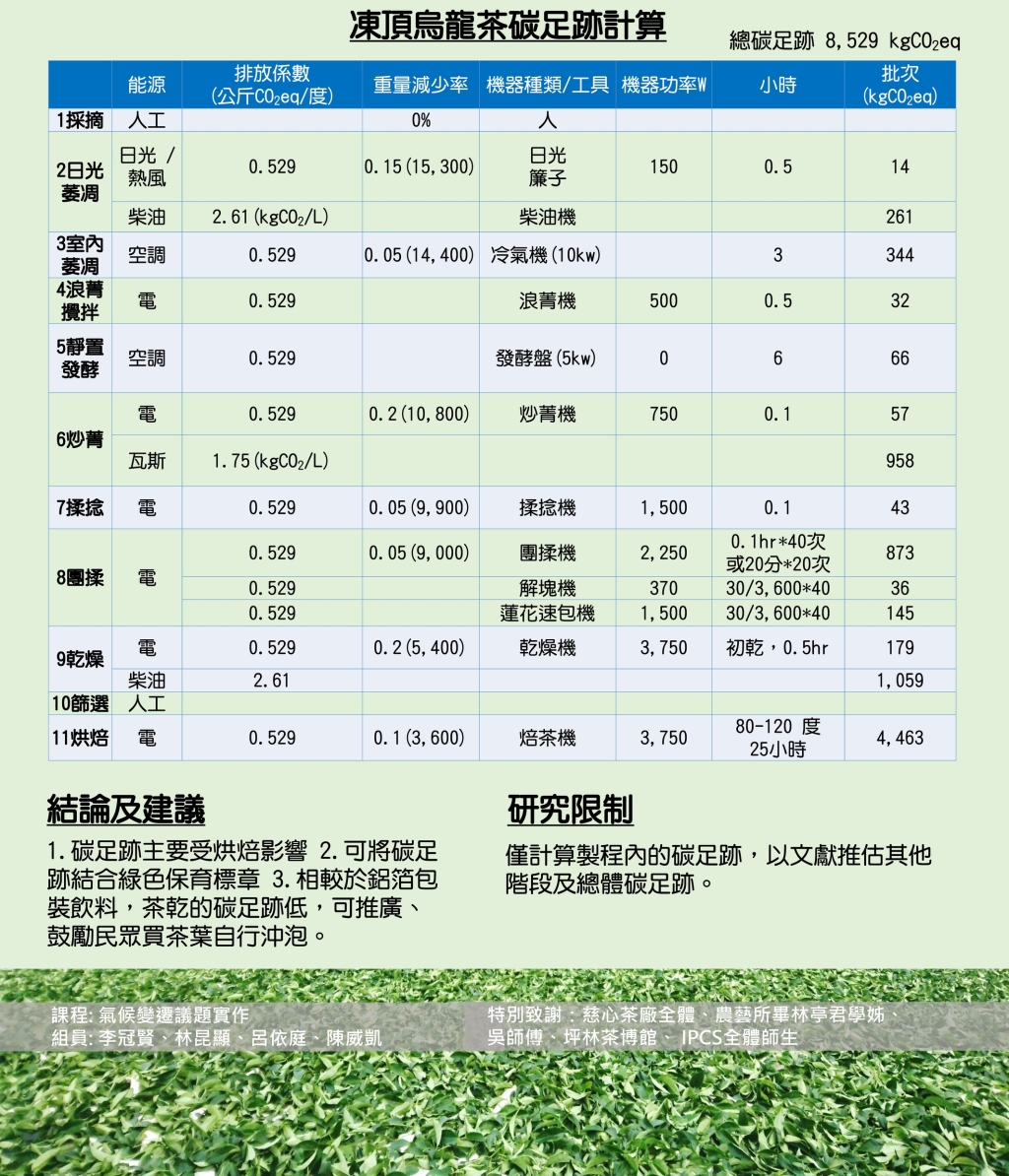
Carbon Footprint of Tongding Oolong Tea

Certification of Cumulative Temperature Model and Forecast of Tea Crop
—茶園科學管理與生長模型之應用探討—
